Our philosophy
Through highly differentiated lessons, all pupils of all abilities always have an activity to complete, irrespective of their pace of learning. All programmes of learning engage pupils in a number of different ways; variety, progressive challenge, and structure are fundamental to our learning philosophy. All learning styles are catered for.
Groupings
Within each scheme there is always a mixture of individual, paired, and group based learning. Where schemes and lessons suit a particular learning style, a predominant style has been adopted. The Organising for the Web unit, for example, involves pupils working in small teams to decide on a band, a team name and to plan their world tour. Pupils also plan a web based timeline together, but research countries individually.
Individual learning takes many forms. From web-based comprehension style exercises designed as a starter activity to get a class on task from the moment they arrive, and to improve literacy, to exercises with multiple questions demanding a high degree of concentration.
Examples:
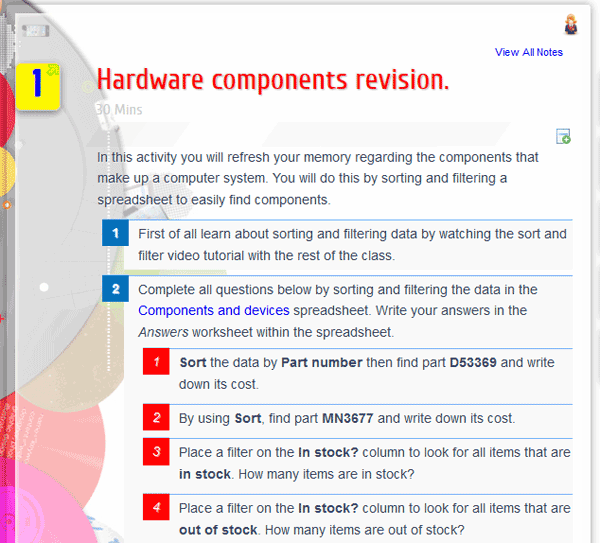
Recommendations are provided within Teacher notes as to how best to structure an activity; independent, paired or grouped. Suggestions are also made on how peer helpers could be used in specific activities to improve progress.

Web presentations
Web based presentations are used to deliver content to allow pupils to complete a subsequent activity. All presentations have a questioning style so that pupils remain active thinkers throughout.
Being browser based, presentations do not have to be downloaded and opened. Instead they load quickly and run instantaneously.
Examples:
Web services
Alongside applications, a number of different web services are used so that pupils experience different methods of completing activities.

Pupils increasingly use web services, whether it be to collaborate online in a gaming environment, or for social networking. It is becoming increasingly important therefore to ensure pupils are aware of the dangers that exist online.
Secret Agent, World Tour and App Planet programmes make regular reference to e-Safety. This is through Teacher notes or through specific activities. e-Safety is built into every relevant scheme; some activities give pupils examples of how to set-up privacy settings so their work can only be shared with pupils of their choosing.
Eduschemes aim to ensure pupils are just as safe online at home, as they are at school.

Video and audio
A number of focused short videos are used to deliver more complex new skills to pupils. After watching a video, all follow-up activities encourage the development of higher order skills as they require application of newly acquired skills as opposed to just the remembering of them.
The videos are proven to help improve pupils' behaviour; pupils know there will be a challenging activity coming next. As the video plays you can actively monitor the class too.
To help ensure pupils spend the majority of their time on-task, videos are on average just four minutes long. The content of all videos is delivered efficiently so pupils maintain interest.
Example:
Self and peer evaluation
Every unit contains an activity, or suggestions, for both self and/or peer evaluation.
Level descriptors are always included for each unit so that pupils know what to aim for. Examples of completed work are provided for many units so pupils know what to aim for.

Kinaesthetic
Physical activity and movement are combined with computing and ICT in a number of schemes. Examples include surveying an IT suite, working out the merits of different sorting algorithms, and a role play to realise the issues of viruses.
Examples: